2022-07-20
2022-07-20
Background: Diabetes is a long-term disease, which is characterised by high blood sugar and has risen as a public health problem worldwide. It may prompt a variety of serious illnesses, including stroke, kidney failure, and heart attacks. In 2014, diabetes affected approximately 422 million people worldwide and it is expected to hit 642 million people in 2040. The aim of this study is to analyse the effect of demographical and clinical characteristics for diabetics disease in Bangladesh.
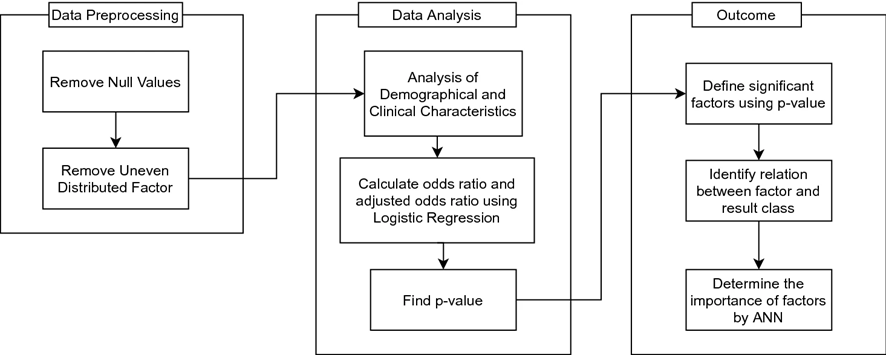
Methods: This study employs the quantitative approach for data analysis. First, we analyse differences in variables between diabetic patients and controls by independent two-sample t-test for continuous variables and Pearson Chi-square test for categorical variables. Then, logistic regression (LR) identifies the risk factors for diabetes disease based on the odds ratio (OR) and the adjusted odds ratio (AOR).
Results: The results of the t-test and Chi square test identify that the factors: residence, wealth index, education, working status, smoking status, arm circumference, weight and BMI group show statistically (p < 0.05) significant differences between the diabetic group and the control group. And, LR model demonstrates that 2 factors ("working status" and "smoking status") out of 13 are the significant risk factors for diabetes disease in Bangladesh.
Conclusions: We believe that our analysis can help the government to take proper preparation to tackle the potentially unprecedented situations in Bangladesh.
Keywords: Diabetes detection, Quantitative analysis, Logistic regression, Significance p-value, Odds ratio, Adjusted odds ratio

背景:糖尿病是一种以高血糖为特征的长期疾病,现已成为世界范围内的公共卫生问题。它可能引发多种严重疾病,包括中风、肾衰竭和心脏病发作等。2014 年,糖尿病影响全球大约 4.22 亿人,预计 2040 年将影响 6.42 亿人。本研究的目的是分析在孟加拉国中人口统计学和临床特征对糖尿病的影响。
途径:本研究采用定量方法进行数据分析。首先,我们通过连续变量的独立双样本 t 检验和分类变量的 Pearson 卡方检验分析糖尿病患者和对照组之间的变量差异。然后,逻辑回归 (LR) 会根据优势比 (OR) 和调整优势比 (AOR) 来确定糖尿病的危险因素。
成果:t检验和卡方检验结果表明:居住地、财富指数、教育程度、工作状况、吸烟状况、臂围、体重和BMI组等因素在糖尿病组和控制组之间有着显著的统计学差异(p < 0.05)。并且,LR 模型表明:13 个因素中的 2 个因素(“工作状态”和“吸烟状态”)是引起孟加拉国糖尿病出现的重要危险因素。
结论:我们相信:我们的分析可以帮助政府采取适当的准备来应对孟加拉国潜在未知的局势。
关键词:糖尿病检测;定量分析;逻辑回归;显著性p值;优势比;调整后的优势比